Enter the number of successes, trials, and the confidence interval of the data set into this point estimate calculator to calculate the best point estimate. The calculator is found below the example.
- Confidence interval calculator
- Percent error calculator
- Absolute value calculator
- Expected Value Calculator
Point Estimate Formula
The following formula can be used to estimate the best point. This is considered the Wilson Estimation.
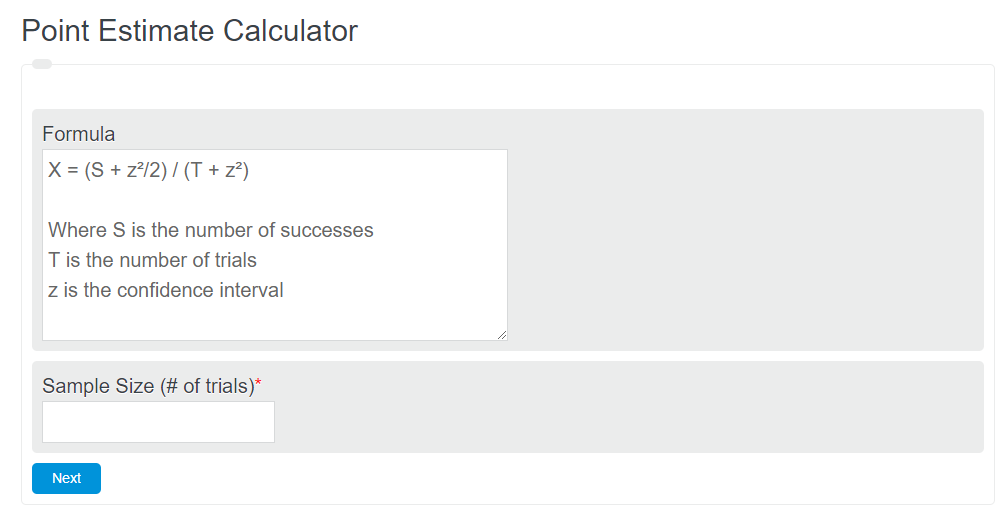
X = (S + z²/2) / (T + z²)
- Where S is the number of successes
- T is the number of trials
- z is the confidence interval
Point Estimate Definition
A point estimate is a single value that is used to estimate an unknown parameter of a population based on sample data. It provides an approximation of the true value of the parameter of interest.
Point estimates are crucial as they allow researchers to make inferences about the entire population using only a sample. They represent the population’s characteristics, providing a glimpse into the unknown. By calculating a point estimate, researchers can gain insights about a population without collecting data from every individual.
Point estimates play a pivotal role in decision-making processes. They are used to estimate parameters such as population means, proportions, or variances.
For example, if a company wants to estimate the average age of its customers, a point estimate can be calculated using a sample of the customers’ ages. This estimate can then be used to guide marketing strategies, product development, or customer service initiatives.
How to calculate a point estimate
The following example is a step-by-step process of calculating a point estimate.
- First, we must determine which missing variables we need to calculate the point estimate. In this case, the variable would be S, the number of successes, T is the number of trials, z is the confidence interval.
- The next step is to find the values for all of those variables.
- Finally, enter all of the information into the formula or calculator above.
FAQ
What is the Wilson Estimation method?
The Wilson Estimation method is a statistical technique used to calculate a point estimate with a given confidence interval. It is particularly useful when dealing with proportions and provides a more accurate estimate than simple proportion calculations, especially for small sample sizes or when the success probability is close to 0 or 1.
How does the confidence interval affect the point estimate calculation?
The confidence interval affects the point estimate calculation by determining the z-value used in the Wilson Estimation formula. A wider confidence interval suggests less certainty about where the true parameter lies, leading to a broader range of potential values. Conversely, a narrower confidence interval indicates a higher level of certainty, resulting in a more precise point estimate.
Why are point estimates important in research and decision-making?
Point estimates are crucial because they provide a single, best-guess value of an unknown population parameter based on sample data. This allows researchers and decision-makers to make informed predictions, conclusions, and strategies without needing data from the entire population. Point estimates are foundational in statistical analysis, aiding in hypothesis testing, confidence interval construction, and more.
Can point estimates be used for all types of data?
Yes, point estimates can be applied to various types of data, including means, proportions, and variances of populations. However, the method of calculation and the formula used may differ depending on the type of data and the specific parameter being estimated. It’s essential to choose the appropriate statistical method and formula to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the point estimate.