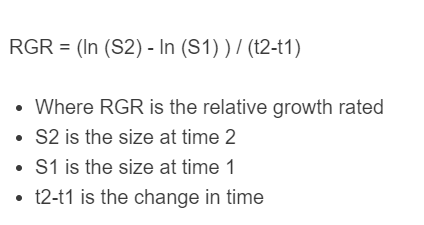Enter the size and two different periods and the total time that has passed between periods into the calculator to determine the relative growth rate.
Relative Growth Rate Formula
The following equation is used to calculate a relative growth rate.
RGR = (ln (S2) - ln (S1) ) / (t2-t1)
- Where RGR is the relative growth rated
- S2 is the size at time 2
- S1 is the size at time 1
- t2-t1 is the change in time
Relative Growth Rate Definition
Relative Growth Rate (RGR) is a quantitative measure used to assess the rate at which a population, organism, or system grows in relation to its initial size.
It is a critical parameter for understanding and comparing growth patterns across various entities. RGR is calculated by dividing the change in size or biomass of an organism over a specific period by its initial size or biomass and then dividing the result by the period.
RGR is a valuable tool for scientists and researchers as it provides insights into the efficiency and vigor of growth. By comparing the growth rates of different individuals, species, or populations, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of their relative performance and adaptability.
Relative Growth Rate Example
How to calculate a relative growth rate?
- First, determine the initial size.
Calculate or measure the initial size.
- Next, determine the final size.
Calculate or measure the final size.
- Next, determine the change in time.
Calculate the total change in time from the initial to final sizes.
- Finally, calculate the relative growth rate.
Calculate the relative growth rate using the formula above.
FAQ
What factors can influence the relative growth rate (RGR) of an organism or population?
Many factors can influence RGR, including environmental conditions, resource availability, genetic factors, and competition. For example, optimal temperature and nutrient availability can enhance growth rates, while competition for resources can reduce them.
How does the relative growth rate differ from the absolute growth rate?
The relative growth rate (RGR) measures the growth of an organism or population in relation to its size, emphasizing the efficiency of growth per unit size. In contrast, the absolute growth rate measures the total increase in size or biomass over a specific period, without accounting for the initial size.
Can the relative growth rate be applied to economic and financial models?
Yes, the concept of RGR can be applied to economic and financial models to evaluate the growth of economies, companies, or investments relative to their size. It helps in understanding the efficiency of growth and comparing entities of different sizes on a standardized basis.
Why is calculating the relative growth rate important in ecological and biological studies?
Calculating the RGR is crucial in ecological and biological studies because it allows researchers to compare the growth rates of different organisms, populations, or species under various conditions. This comparison can reveal insights into the adaptability, health, and vigor of organisms, contributing to a better understanding of ecological dynamics and evolutionary processes.