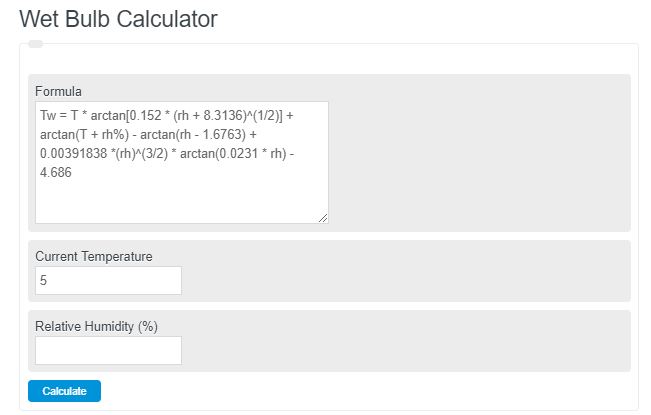
Enter the current temperature and relative humidity. The calculator will evaluate and display the estimated wet bulb temperature at those conditions.
- Air Density Calculator
- Dew Point Calculator
- Snow Day Chance
- Swamp Cooler Efficiency Calculator
- Water Saturation Calculator
Wet Bulb Formula
The following formula is used to calculate the wet-bulb temperature.
Tw = T * arctan[0.152 * (rh + 8.3136)^(1/2)] + arctan(T + rh%) – arctan(rh – 1.6763) + 0.00391838 *(rh)^(3/2) * arctan(0.0231 * rh) – 4.686
- Where TW is the wet-bulb temperature
- T is the current temperature
- rh is the relative humidity (%)
What is Wet-Bulb Temperature?
Wet-bulb temperature is a meteorological parameter used to measure the cooling effect of evaporation on the human body. It is determined by wrapping a wet cloth around the bulb of a thermometer and measuring the temperature drop caused by the evaporation of water from the cloth.
This measurement provides valuable insights into the potential health risks associated with heat stress and the effectiveness of various cooling methods.
The human body relies on evaporative cooling through sweat evaporation to maintain a stable internal temperature. When the air becomes saturated with moisture, the evaporation process slows, and the body’s ability to cool itself becomes compromised.
Consequently, high wet-bulb temperatures indicate reduced evaporative cooling efficiency and increased risk of heat-related illnesses.
How to calculate wet bulb temperature
- First, determine the current temperature
Measure the current temperature using a thermometer.
- Next, determine the current relative humidity
This humidity is measure as a %
- Finally, calculate the wet bulb
Using the current temperature and the humidity, calculate the wet-bulb temperature.
FAQ
What factors affect wet-bulb temperature readings?
Wet-bulb temperature readings can be influenced by several factors, including the air’s relative humidity, the ambient air temperature, and the wind speed. High humidity and low wind speed can result in higher wet-bulb temperatures, indicating a reduced capacity for evaporative cooling.
How is wet-bulb temperature relevant to heat stress and human health?
Wet-bulb temperature is a critical indicator of heat stress because it reflects the maximum efficiency of the human body to cool itself through perspiration and evaporation. High wet-bulb temperatures can lead to a higher risk of heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion and heat stroke, especially in vulnerable populations and those engaged in strenuous activities.
Can wet-bulb temperature be used to predict weather conditions?
While wet-bulb temperature is primarily used to assess the cooling effect of evaporation on the human body, it can also provide insights into weather conditions, particularly in forecasting the potential for rain or thunderstorms. High wet-bulb temperatures in conjunction with other meteorological data can indicate a high moisture content in the air, which may precede precipitation events.