This calculator determines the final volume of gas given the initial temperature, initial volume, and final temperature. Enter these three values into the calculator below to determine the final volume.
- Boyle’s Law Calculator
- Ideal Gas Law Calculator
- Thermal Expansion Calculator
- Thermal Energy Calculator
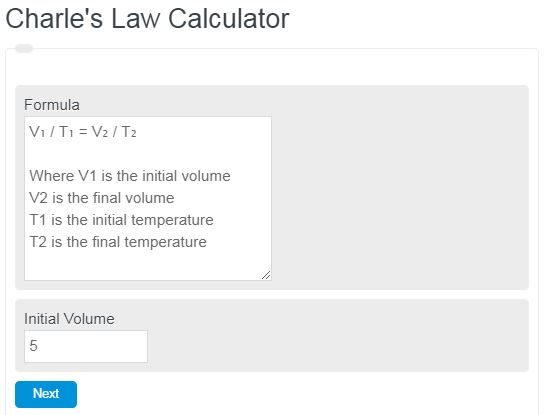
Charle’s Law Formula
The following formula describes the equation derived from Charle’s Law of ideal gases.
V₁ / T₁ = V₂ / T₂
- Where V1 is the initial volume
- V2 is the final volume
- T1 is the initial temperature
- T2 is the final temperature
Through this equation, we can re-arrange the variables to solve for the final volume of a gas going through a temperature and volume change. That equation is displayed as
(V₁ / T₁)*T₂ = V₂
It’s important to note, as with most laws involving gases, that these equations only work with ideal gases. Ideal gases behave in a way that lets scientists form clean equations for calculating their parameters.
What is Charle’s Law?
Charles’s Law is a fundamental principle in the field of thermodynamics that describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas.
According to Charles’s Law, if the pressure remains constant, the volume of a gas will increase as its temperature increases, and vice versa. This means that when a gas is heated, its molecules gain energy and move more vigorously, causing them to collide with each other and the container walls more frequently, thus increasing the volume of the gas.
Conversely, when a gas is cooled, its molecules lose energy and move less vigorously, resulting in fewer collisions and a decrease in volume.
Charles’s Law helps us understand and predict how gases respond to changes in temperature, which is crucial in various applications such as heating and cooling, and understanding the behavior of gases in everyday life.
How to calculate final volume using Charle’s Law?
how to calculate final volume?
- First, determine the initial volume and temperature.
Measure the initial volume and temperature of the gas.
- Next, determine the final temperature.
Measure the final temperature of the gas.
- Finally, calculate the final volume.
Using the second equation above, calculate the final volume.
FAQ
What are ideal gases?Ideal gases are theoretical gases composed of many randomly moving point particles that do not interact except when they collide elastically. The concept simplifies the mathematical modeling of chemical reactions.
Why does Charles’s Law only apply to ideal gases?Charles’s Law applies to ideal gases because it assumes that there are no forces of attraction between the molecules, which is not the case for real gases, especially under high pressure or at low temperatures.
How do temperature changes affect gas volume in real-life applications?In real-life applications such as air conditioning, refrigeration, and automotive engines, temperature changes can cause significant changes in gas volume, affecting performance and efficiency based on principles like Charles’s Law.
Can Charles’s Law be used to calculate gas pressures?While Charles’s Law itself relates volume and temperature, it can be combined with Boyle’s Law in the ideal gas law equation to calculate changes in pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas.