Calculate the best price of your product based on the price elasticity of demand. Use this calculator to determine the elasticity of your product.
- Maximum Revenue Calculator
- Break Even Point Calculator
- Return on Equity Calculator
- Cross Price Elasticity Calculator
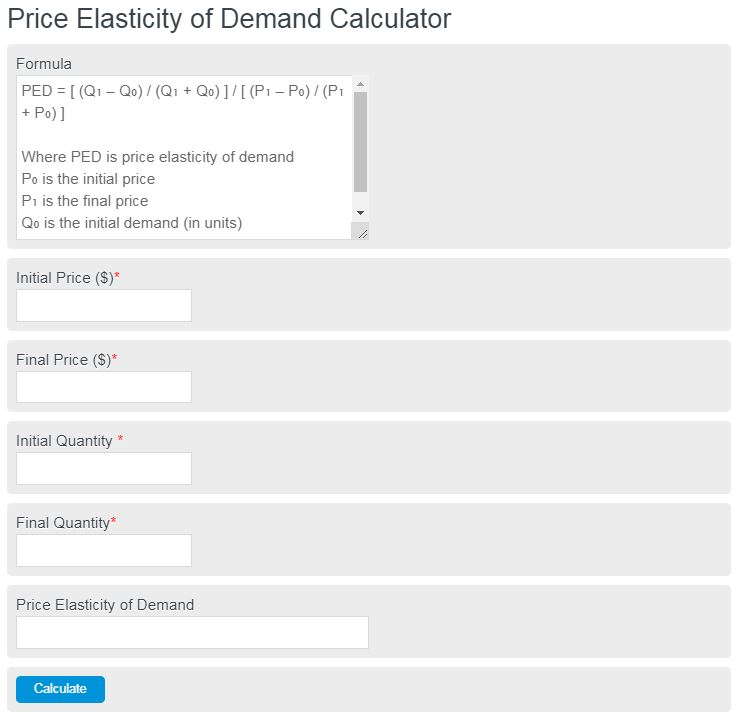
Price Elasticity of Demand Formula
The following formula can be used to calculate the price elasticity of demand:
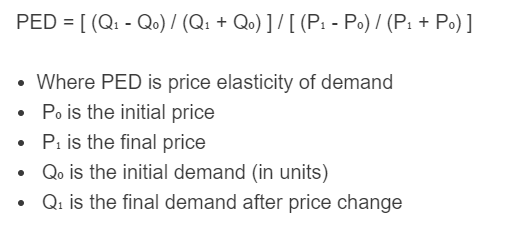
PED = [ (Q₁ - Q₀) / (Q₁ + Q₀) ] / [ (P₁ - P₀) / (P₁ + P₀) ]
- Where PED is the price elasticity of demand
- P₀ is the initial price
- P₁ is the final price
- Q₀ is the initial demand (in units)
- Q₁ is the final demand after the price change
The higher the magnitude elasticity, the higher the resulting increase in revenue will be with a price decrease. A low elasticity means that a price decrease will only result in a small increase in revenue.
Price Elasticity of Demand Definition
Price elasticity of demand is a measure that quantifies the responsiveness of consumers to changes in the price of a good or service.
It is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in price. This value can be positive, negative, or zero.
The significance of price elasticity of demand lies in its ability to determine the sensitivity of consumers’ demand to price fluctuations. A higher elasticity suggests that a small price change will result in a proportionally larger change in quantity demanded, indicating a relatively elastic demand.
On the other hand, a lower elasticity signifies a smaller change in quantity demanded in response to a price change, indicating inelastic demand.
Understanding the price elasticity of demand is crucial for businesses and policymakers as it helps them make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, revenue projections, and taxation policies.
By knowing the elasticity, firms can assess the potential impact of price changes on their sales and revenues.
If demand is elastic, a price decrease may lead to a substantial increase in quantity sold, resulting in higher total revenue. If demand is inelastic, a price increase may lead to a smaller decline in quantity demanded, enabling firms to increase revenue despite selling fewer units.
How to calculate the price elasticity of demand
Lets’s take a look at an example of how one might use this calculator or calculate the price elasticity of demand.
First, let’s assume you have a product that you have been selling for a year. That product currently costs $5.00 and sells at 10 units per day.
Next, we want to experiment with decreasing the price of this item so we chose to lower the item to $4.50. This results in an increase in sales to 15 units per day.
Using the calculator above, we find that the price elasticity of demand is equal to -3.8. As mentioned above the greater the magnitude the greater the elasticity. Even though the result is negative, the magnitude is much greater than 1, which is what matters.
PEOD and your Business
The reason PED is important for running your business is because of its effect on revenue. Revenue, along with costs, is the driving force of business performance. If you can drastically increase your business performance through a quick understanding and research of PED, then it’s worth your time.
PED can be broken down into two separate categories. The price effect and the quantity effect.
The price effect is the analysis of how a change in price will change total revenue. For inelastic goods, an increase in price will lead to an increase in revenue and vise versa. For elastic goods, this is not always true. An increase in price may lead to a drastic decrease in sales and revenue.
The quantity effect is described as the lowering in total units sold due to a higher price and an increase in units sold with a decrease in price.
It’s important to understand that the optimal price point of a unit is constantly changing. This means that the PED must be researched and analyzed monthly to understand the optimal price point.