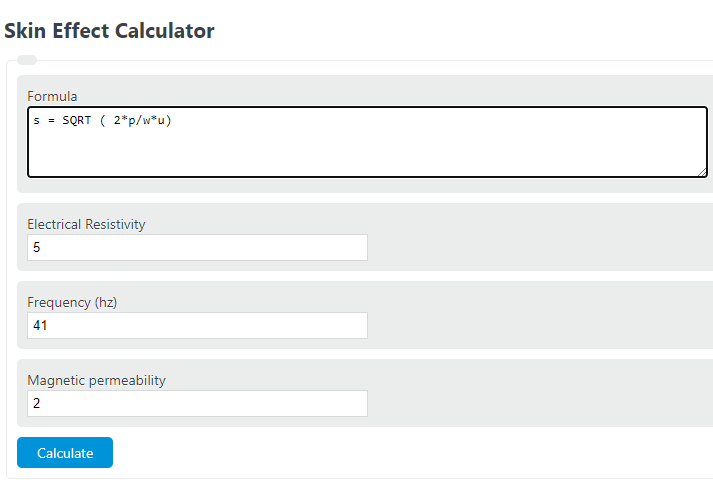
Enter the electrical resistivity, angular frequency, and magnetic permeability into the calculator to determine the skin depth.
- Resistivity Calculator
- Angular Frequency Calculator
- Magnetic Flux Calculator
- Wire Ampacity Calculator
Skin Effect Formula
The following formula is used to calculate a skin effect depth.
s = SQRT ( 2*p/w*u)
- Where s is the skin effect depth
- p is the electrical resistivity.
- w is the angular frequency (2*pi*f)
- u is the magnetic permeability
Skin Effect (physics) Definition
Skin effect is a phenomenon in physics that occurs when alternating current (AC) flows through a conductor.
When an AC current passes through a conductor, the current tends to concentrate near the surface of the conductor, rather than flowing uniformly through the entire cross-section. This concentration of current near the surface is known as the skin effect.
The skin effect results from the interaction between the AC current and the magnetic field it creates. As the AC current changes direction, it induces a magnetic field around the conductor. This magnetic field, in turn, generates an opposing electric field within the conductor.
The combination of these fields causes the AC current to flow primarily near the surface of the conductor.
The significance of the skin effect lies in its impact on the efficiency and performance of electrical systems.
Since the majority of the current flows near the surface of the conductor, the effective cross-sectional area for current flow decreases as the frequency of the AC current increases.
This means that at higher frequencies, the conductor effectively becomes less conductive.
The skin effect leads to increased resistance and power losses in the conductor. These losses manifest as heat, which can be detrimental in various applications.
For instance, in power transmission lines, the skin effect causes power dissipation, reducing the overall efficiency of the system. Similarly, in high-frequency applications like radio frequency (RF) circuits, the skin effect can cause signal distortion and loss.
To mitigate the negative effects of the skin effect, conductors used in high-frequency applications are often designed with larger surface areas.
Skin Effect Example
How to calculate skin effect depth?
- First, determine the resistivity.
Measure or calculate the resistivity of the system.
- Next, determine the angular frequency.
This is equal to 2*pi*f, where f is the frequency in hz.
- Next, determine the magnetic permeability.
Calculate the magnetic permeability.
- Finally, calculate the depth.
Calculate the depth of the skin effect using the formula above.
FAQ
How does frequency affect the skin effect?
Frequency directly influences the skin effect; as the frequency of the alternating current increases, the skin depth decreases. This means that the current concentrates more closely to the surface of the conductor at higher frequencies.
Why is the skin effect important in electrical engineering?
The skin effect is crucial in electrical engineering because it affects the resistance and efficiency of conductors in AC circuits. Understanding and mitigating the skin effect is essential for designing efficient power transmission systems and high-frequency electronic devices.
Can the skin effect be eliminated?
While the skin effect cannot be completely eliminated in conductors carrying alternating current, it can be minimized. This is often achieved by using conductors with larger surface areas or by employing materials with higher magnetic permeability for the specific application frequencies.