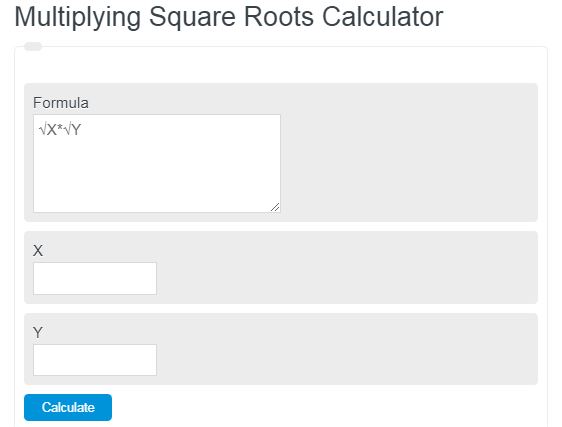
Enter two numbers, X and Y, into the calculator below to determine the value of the square root of x times the square root of y.
- Cube Root Calculator
- Exponent Calculator
- Quadratic Formula Calculator
- Fraction Exponent Calculator
- Square Root Curve Calculator
Multiplying Square Roots Formula
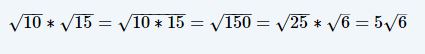
Multiplying square roots is typically done in one of two ways. One is through the method described above. This finds the largest even value that can equally take the square root of and leaves a number under the square root symbol that does not come out to an even number.
Multiplying Square Roots Definition
Multiplying square roots involves multiplying the results of the individual square roots.
Example Problem
Let’s look at an example of multiplying the square roots of 3 different numbers.
- First, the numbers are given as 3,4, and 5 respectively,
- Next, we need to multiply the 3 numbers together. 3*4*5= 60.
- Finally, take the square root of the result from step 2. Sqrt (60) = 7.7459.
FAQ
What is the significance of the square root in mathematics? The square root function is fundamental in mathematics, representing a number that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. It’s crucial for solving quadratic equations, understanding geometric shapes, and in various fields such as physics and engineering for calculating distances and forces.
Can square roots be negative? In the realm of real numbers, square roots of negative numbers are not defined because no real number multiplied by itself will result in a negative number. However, in complex numbers, the square root of a negative number is defined, with the square root of -1 represented as i, an imaginary unit.
How does multiplying square roots differ from adding them? Multiplying square roots involves multiplying the numbers under the root and then taking the square root of the product, which can simplify the expression. Adding square roots, however, can only be simplified if the radicands (the numbers under the root) are the same; otherwise, they must be expressed as a sum of roots.
Are there any special cases when multiplying square roots? Yes, when multiplying square roots of perfect squares (numbers that are squares of integers), the result simplifies to an integer or a rational number. Additionally, multiplying conjugate pairs of square roots (e.g., sqrt(a) and -sqrt(a)) results in rational numbers, as the product is the difference of squares.