Enter the voltage, current, and power factor into the calculator below to determine the total electric power of a system.
- Capacity Factor Calculator
- Electric Field Calculator
- Battery Capacity Calculator
- Electric Potential Calculator
- Electricity Load Calculator
- Electrostatic Potential Energy Calculator
- Electric Energy Calculator
- Electrical Length Calculator
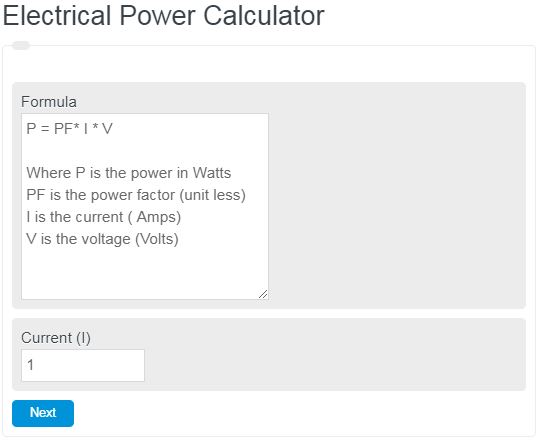
Electrical Power Formula
The following equation can be used to determine the total electrical power output of a system (Watts)
P = PF* I * V
- Where P is the power in Watts
- PF is the power factor (unitless)
- I is the current ( Amps)
- V is the voltage (Volts)
In this case, the power factor is a measure of the efficiency of an AC system. In short, AC systems work with current and voltage varying with time. This is usually in some sinusoidal propagation. Essentially, if the current and voltage are not in sync, then the output will be less than the max output of power. This is where the power factor comes in. If the current and voltage are in sync then the power factor is 1. If they are not, then the power factor is less than 1. There are few cases where the power factor can be greater than 1, but these are few and far between. Keep in mind the units displayed in the list above to make sure your units are the same.
Electrical Power Definition
Electrical Power is defined as the total electrical energy transfer per unit of time of an electrical circuit or system.
How to calculate electrical power?
How to calculate electrical power?
- First, determine the power factor.
The power factor is in essence the efficiency of the electrical system.
- Next, determine the voltage.
Determine the voltage of the system.
- Next, determine the amps.
Measure the amps of the system.
- Finally, calculate the electrical power.
Use the equation provided above to calculate the electrical power.
FAQ
Electrical Power is defined as the total electrical energy transfer per unit of time of an electrical circuit or system.