Enter the thermal conductivity constant, the temperature difference, and the change in distance to calculate the heat flux of an object.
- Enthalpy Calculator
- Latent heat Calculator
- Specific Heat Calculator
- Flux Density Calculator
- LMTD (Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference) Calculator
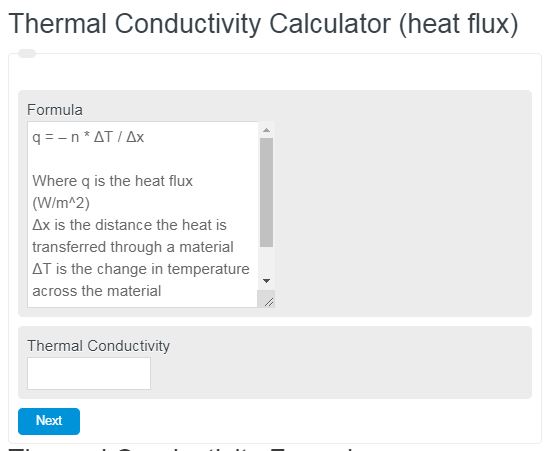
Thermal Conductivity Formula
The following equation calculates the heat flux, q, of a material. This equation is driven and derived through Fourier’s law of heat flux.
q = - n * ΔT / Δx
- Where q is the heat flux (W/m^2)
- Δx is the distance the heat is transferred through a material
- ΔT is the change in temperature across the material
- n is the thermal conductivity of the material
The units for heat flux are watts per meter squared or, in other words, energy per area. This makes logical sense in that a change in temperature across an object is the same as the change in energy across the area of the object. In this formula, it’s important to remember that the units for x need to be in meters, and the units for temperature need to be in Kelvin.
What is Thermal Conductivity?
Thermal conductivity refers to the property of a material that determines its ability to conduct heat. It measures how efficiently heat can flow through a substance when there is a temperature difference between two points.
In simpler terms, thermal conductivity is a measure of how well a material can transfer heat. It quantifies the rate at which heat energy is conducted through a material.
The ability of a substance to conduct heat is crucial in various applications and industries. For instance, in engineering, thermal conductivity plays a vital role in designing and manufacturing efficient heat transfer systems. It helps engineers select the appropriate materials for applications such as heat exchangers, radiators, and insulation.
Understanding thermal conductivity is also essential in fields like materials science and construction.
It allows researchers and engineers to evaluate and compare materials based on their heat transfer properties. This knowledge enables the development of more effective insulating materials, which can enhance energy efficiency in buildings and reduce heat loss or gain.
Thermal conductivity is significant in everyday life as well. It affects the performance of household appliances such as refrigerators, ovens, and air conditioners.
By using materials with high thermal conductivity in heat sinks or cooling systems, these appliances can efficiently dissipate heat, ensuring their optimal functionality.
How to calculate thermal conductivity?
How to calculate thermal conductivity?
- First, determine the change in temperature.
Through an experiment you have set up, measure the change in temperature of a material.
- Next, determine the distance.
Measure the distance the heat has travelled.
- Next, determine the heat flux.
Measure the total heat flux through the material.
- Finally, calculate the thermal conductivity.
Using the formula above, re-arrange the equation to solve for thermal conductivity.
FAQ
Thermal conductivity is a measure of the ability or resistance of a material to transfer heat through conduction.